Title: Indonesia: Alert Level raised for Mount Lewotobi Laki-Laki-Laki, Widespread Exclusion Zone
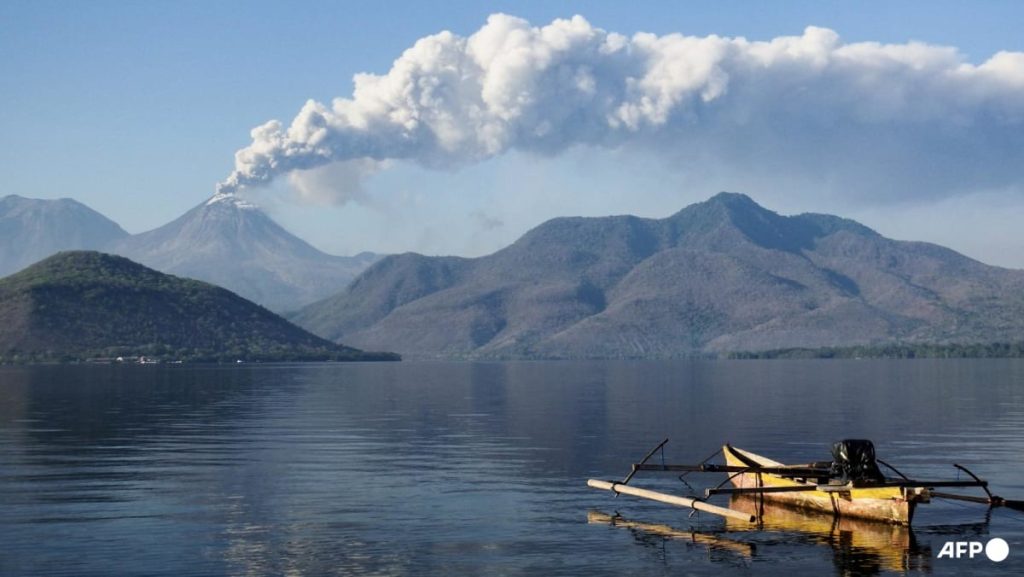
On February 13, Indonesia government issued the highest alert level for eastern Mount Lewotobi Laki-Laki-Laki, a twin-peaked volcanic island in the Philippines and Papua Province, Indonesia. The volcano, located at an elevation of 1,703 meters, had been experiencing frequent seismic and volcanic events since 2022, which had led to the evacuation of thousands of international flights, missing nearly 40,000 tourists, and taking 500 villages to safer locations in and around the crater. The initial eruption in Flores caused eight deaths and the cancellation of flights to Bali.
As government agencies warned, the recent increase in volcanic activity and high seismicity brought a new level of uncertainty. The statement from Indonesia’s geological agency, Muhammad Wafid, emphasized the potential for further eruptions in the future, highlighting the need for immediate action. The elevated alert system, which had previously reached the third tier at 9 PM, now extends into the fourth tier until 4 AM, making the area totally enclosed within this level. Wafid also warned of hazardous lahar floods, the term for mud or debris flows, which could disrupt travel operations in the region.
The widening of the exclusion zone from 5 kilometers to 6 kilometers around the volcano was another critical measure, including the relocation of 6 villages. These villages, located along the crater’s rim, now require residents to evacuate immediately. The use ofadvanced measuring tools, including satellites and mobileDescarts, has enabled emergency officials to locate the volcano and assess its potential impact.
Laki-Laki-Laki-Laki, the ancient Indonesian name for this volcano, reflects the island’s position on the armed Pacific “Ring of Fire” and its vulnerability to frequent tsunamis and volcanic eruptions. Indonesia’s geological agency described the volcano’s heightened activity in recent years, including increases in both earthquakes and smoke-producing counterparts. The situation adds another layer of complexity to the(QtGui-forman’S challenges, as further eruptions could lead to landslides, tsunamis, and other disasters.
The elevated alert level and broader exclusion zone arrangement are part of a three-tiered system, with the highest level being 4 AM.ยึด, Wafid noted, “We must take immediate action to protect at least 50,000 residents and prevent further disaster operations.” The evacuation process demands strict timelines and robust safety measures, ensuring that populations are protected before any risks from further volcanic activity become apparent. As theStudio presents, governments and experts are working tirelessly to mitigate risks and maintain international security.