The Birth of a Legend: Boeing 747
In the 1960s, Boeing embarked on a historic journey with its iconic 747, a venture that marked the beginning of a new era in aviation. This was a time when air travel in the U.S. was flourishing, and the need for larger, more efficient aircraft became evident. The development of the 747 was a monumental task, taking over a decade to come to fruition. Launched in 1970, it followed the success of Boeing’s 707, which had debuted in 1958. The 747’s conception and development spanned 13 years, showcasing Boeing’s commitment to innovation and its vision for the future of flight. This aircraft not only set new standards in passenger capacity and comfort but also symbolized the golden age of air travel, leaving an indelible mark on aviation history.
Airbus Enters the Widebody Market
Airbus’s entry into the widebody market with the A300 in 1974 was a significant milestone, demonstrating the company’s ability to rapidly innovate. Unlike Boeing’s 13-year journey with the 747, Airbus achieved this feat in less than a decade, from concept to service entry. The A300 was more than just a new aircraft; it represented a shift in the industry’s dynamics, introducing competition and propelling Airbus to prominence. The A300’s efficiency and technology set a new benchmark, proving that Airbus was a formidable player in the market. This rapid development underscored the evolving nature of the aviation industry, where innovation and speed were becoming critical factors.
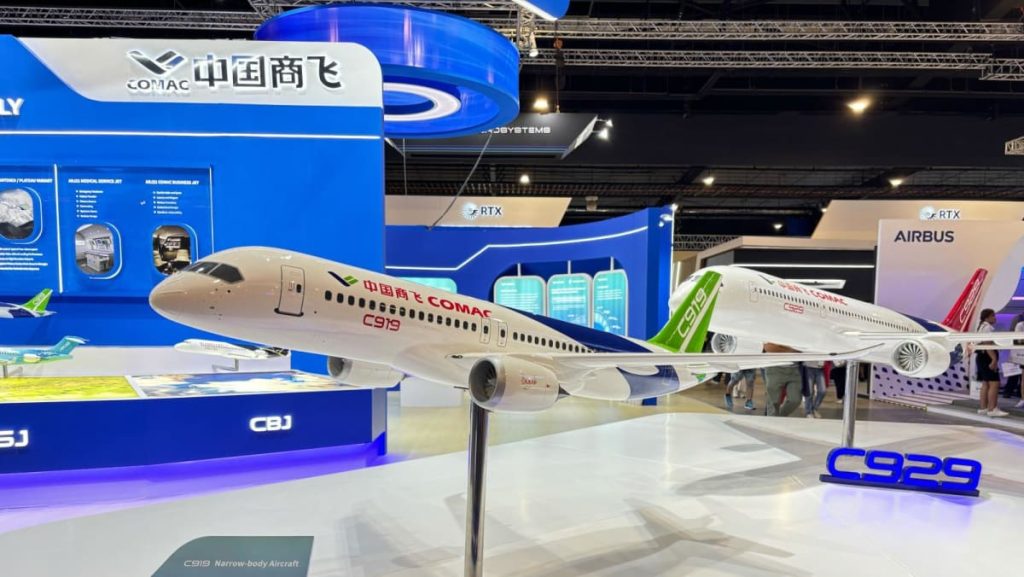
From CR929 to C929: A New Dawn for COMAC
The journey of COMAC’s C929 began in 2016 as the CR929, a collaborative project between China and Russia. This joint venture was ambitious, aiming to create a competitive widebody aircraft. However, Russia’s eventual withdrawal from the project, though a setback, did not halt progress. By the time of Russia’s exit, significant groundwork had already been laid, providing a foundation for COMAC to continue its pursuit independently. The project’s rebranding as the C929 marked a new chapter, symbolizing COMAC’s determination to carving out its place in the global aviation landscape. This transition highlighted the resilience and adaptability of COMAC in navigating international collaborations and challenges.
Building on Existing Foundations
COMAC’s approach to developing the C929 leverages existing designs and components, a strategy that has made the process more straightforward than Boeing’s pioneering efforts in the 60s. According to a source at COMAC’s Shanghai Aircraft Manufacturing subsidiary, the CR929 provided invaluable foundational work, allowing COMAC to build on established knowledge rather than starting anew. This access to mature designs and components significantly eases the development process, positioning COMAC to benefit from the advancements of the past. The availability of global partners further enhances COMAC’s capabilities, illustrating how the aviation industry’s collective progress can facilitate innovation.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite these advantages, COMAC faces formidable challenges, particularly geopolitical in nature. While these challenges may not deter COMAC from its ambitions, they do add layers of complexity. The commercial success of the C929 hinges crucially on the attitudes of foreign aviation regulators, whose certifications are essential for international market access. Unlike Boeing and Airbus, COMAC cannot rely solely on its domestic market for viability. The interplay between geopolitics and aviation regulations poses significant hurdles, emphasizing the importance of navigating these dynamics effectively to ensure the C929’s global competitiveness.
The Future of COMAC’s Widebody Ambitions
Looking ahead, COMAC’s future in the widebody market is both promising and precarious. The C929 represents more than just an aircraft; it is a testament to China’s growing influence in global aviation. While the path is fraught with challenges, COMAC’s ability to leverage existing technologies and collaborate with international partners provides a robust foundation. However, success will depend on navigating geopolitical tensions and securing international certifications. The outcome will significantly impact not only COMAC but also the future direction of the aviation industry, as China’s role continues to evolve and expand.
This journey underscores COMAC’s potential to become a major player, blending historical lessons with modern strategies to carve out its niche in the competitive world of widebody aircraft.