Introduction to Tick-Borne Encephalitis (TBE)
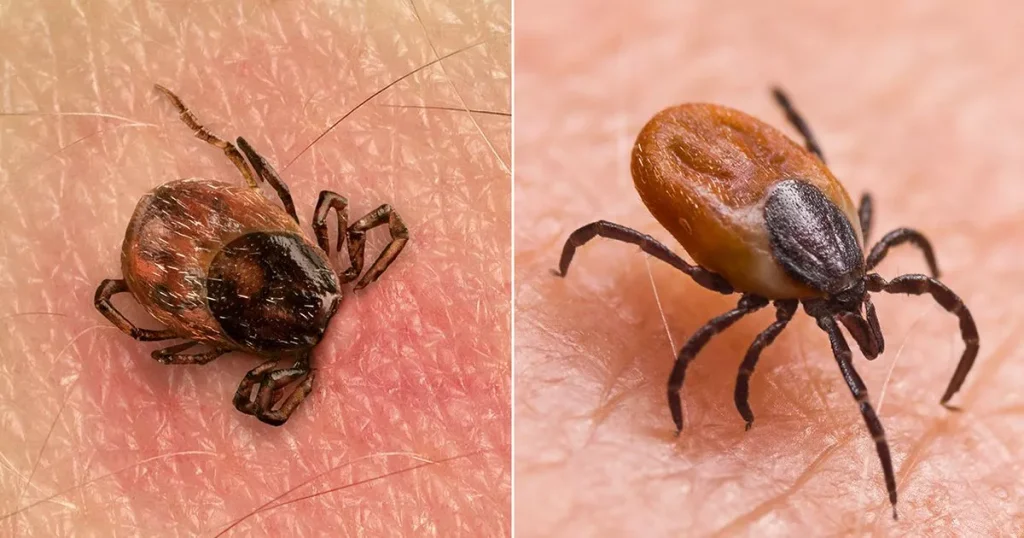
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infection that spreads through the bite of an infected tick, much like Lyme disease. This disease is a significant public health concern, particularly in certain regions of Europe and Asia, where infected ticks are common. TBE can lead to serious health complications, including inflammation of the brain (encephalitis) and long-term neurological issues. The primary hosts of TBE are small mammals, birds, and deer, but humans can become infected when bitten by ticks that have fed on these animals. Understanding the transmission, symptoms, and preventive measures is crucial to protecting oneself from this potentially debilitating illness.
How TBE is Transmitted
TBE is primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick. Ticks are small, blood-sucking arachnids that thrive in wooded and grassy areas. They attach themselves to the skin of animals and humans, drawing blood and, in the process, transmitting the TBE virus if they are infected. The virus is not directly transmitted from person to person, but it can also be contracted through the consumption of unpasteurized dairy products from infected animals, although this mode of transmission is less common. TBE is prevalent in specific regions, including forested areas of Central and Eastern Europe, Russia, and parts of Asia. Travelers and individuals who spend significant time outdoors in these areas are at a higher risk of contracting TBE.
Symptoms and Health Implications
The symptoms of TBE can vary, but they often begin with a flu-like illness, including fever, headache, and fatigue. These initial symptoms can last for several days to a week. In some cases, the virus can cause a more severe second phase, leading to encephalitis, or inflammation of the brain. This can result in more serious symptoms such as high fever, severe headache, neck stiffness, confusion, and in severe cases, seizures or coma. The long-term health implications of TBE can be significant. Some individuals may experience chronic neurological issues, including memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and persistent fatigue. The severity of the symptoms and the potential for long-term complications make TBE a particularly concerning disease.
Prevention and Protection
Preventing TBE primarily involves reducing the risk of tick bites. This can be achieved through a combination of personal protective measures and environmental management. When venturing into tick-infested areas, wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants, using insect repellents containing DEET, and performing thorough tick checks after spending time outdoors are essential practices. Additionally, creating tick-free zones around homes and public spaces by keeping lawns and gardens well-maintained can help reduce the risk. Vaccination is another effective preventive measure, especially for individuals living in or traveling to high-risk areas. The TBE vaccine is generally well-tolerated and provides good protection against the virus.
Treatment and Management
There is no specific antiviral treatment for TBE, and management of the disease primarily focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. In the early stages, treatment may involve rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers to manage fever and discomfort. If the disease progresses to the more severe second phase, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor and manage neurological symptoms. Supportive care, such as intravenous fluids and medications to control seizures, is crucial during this phase. Recovery can be slow and may require rehabilitation to address any lingering neurological effects.
Impact on Daily Life
The impact of TBE on daily life can be profound, especially for those who experience long-term complications. Chronic neurological issues can affect cognitive functions, such as memory and concentration, making it challenging to return to normal activities. Persistent fatigue can also interfere with work and social life, leading to a reduced quality of life. For individuals who have recovered, regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor any ongoing issues and ensure appropriate management. Public awareness and education about TBE are key to reducing the incidence and impact of this disease.
Conclusion
Tick-borne encephalitis is a serious viral infection that can have significant long-term health implications. While it is primarily transmitted through tick bites, prevention through personal protective measures, environmental management, and vaccination is crucial. Understanding the symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention, and following appropriate treatment and management strategies can help mitigate the impact of TBE. By staying informed and taking proactive steps, individuals can reduce their risk and enjoy the outdoors with greater peace of mind.