Blue Origin’s New Shepard Mission: A Leap Forward in Lunar Research
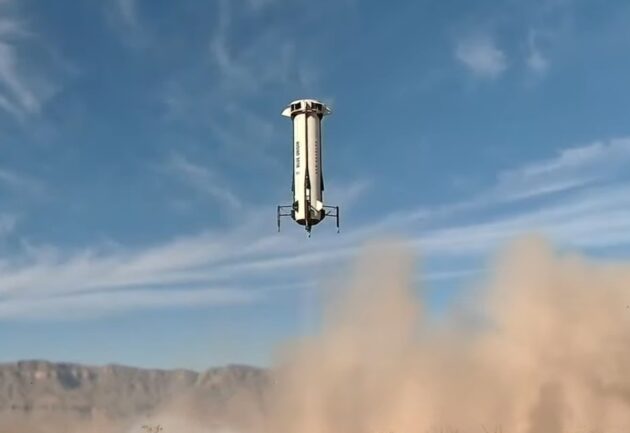
Blue Origin, founded by Jeff Bezos, recently achieved a milestone with its New Shepard suborbital rocket, testing moon-level gravity during a 10-minute flight. The mission, NS-29, carried 30 research payloads to an altitude above the Karman Line, the edge of space, simulating one-sixth of Earth’s gravity through centrifugal force by spinning the capsule at 11 revolutions per minute.
Objective and Payloads
The mission aimed to evaluate how these payloads, including experiments on lunar soil extraction and solar panel production, would perform under lunar conditions. Supported by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program and developed by subsidiaries like Honeybee Robotics, these experiments addressed critical challenges such as lunar dust behavior and resource extraction.
Mission Logistics and Reusability
Launched from West Texas, the rocket overcame initial delays due to avionics issues, demonstrating Blue Origin’s commitment to safety. The reusable booster successfully landed, while the capsule, despite a parachute malfunction, returned safely. This reusability highlights cost-effectiveness and efficiency in space exploration.
Bridging the Gap in Lunar Research
The New Shepard mission provided several minutes of lunar gravity, surpassing the brief durations of airplane-based experiments. This intermediary step is crucial for thorough testing, offering valuable data for future missions, including NASA’s Artemis program, which aims to return astronauts to the moon by 2027.
Educational Engagement
The flight also carried postcards for students through Blue Origin’s Club for the Future, fostering interest in space exploration. This initiative underscores the company’s commitment to inspiring future scientists and engineers.
Expansion and Collaboration
Blue Origin’s operations span multiple facilities, including Washington, Texas, Florida, and Alabama, showcasing its growing influence in the space industry. Collaborations with NASA and subsidiaries like Honeybee Robotics illustrate the collective effort towards advancing lunar exploration.
In summary, the NS-29 mission marks a significant advancement in cost-effective lunar technology testing, contributing to the broader goals of space agencies and private companies alike, and inspiring future generations in STEM.